Book Appointment Now

Mastering the 5 Phases of Focused Note Taking
Struggling to keep up with your studies? You’re not alone. Mastering the 5 phases of focused note taking can transform how you learn.
Focused note taking involves systematically capturing, organizing, and applying information. This article delves into the five focused note-taking phases, providing practical strategies to master each phase.
Get ready to elevate your learning game!
Key Takeaways
- Focused note taking is a structured approach to capturing and utilizing information effectively.
- The five phases include Previewing and Planning, Active Listening and Recording, Reviewing and Revising, Summarizing and Synthesizing, and Applying and Assessing.
- Two-column notes or the Cornell method help organize thoughts, making it easier for students to understand complex ideas. They encourage active learning by connecting new information with what the student already knows.
- Engaging in focused note-taking enhances retention and understanding of material. It encourages active participation in learning through summarizing, reflecting, and questioning.
- Teachers play a crucial role in implementing focused note-taking by introducing different formats, demonstrating digital tools, and guiding students through the process. This turns passive listeners into actively engaged learners.
Phase 1: Previewing and Planning
Importance of Preparation
The first phase of focused note taking is Previewing and Planning. Preparation is crucial as it sets the stage for effective note-taking. By previewing the material, you can identify key themes and concepts, making it easier to focus on important information during the note-taking process.
Techniques for Previewing Material
- Skimming: Quickly skim through the material to get an overview of the content.
- Identifying Key Sections: Look for headings, subheadings, and highlighted terms.
- Setting Objectives: Determine what you aim to achieve from the note-taking session.
Setting Goals for Note-Taking Session
Establish clear goals for your note-taking session. Are you looking to understand a specific concept, memorize facts, or prepare for a discussion? Setting objectives will help you stay focused and organized.
Phase 2: Active Listening and Recording
Strategies for Active Listening
Active Listening is the second phase of focused note taking. It involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the information being presented. This phase is critical for capturing accurate and relevant notes.
- Stay Engaged: Maintain eye contact with the speaker and avoid distractions.
- Ask Questions: If possible, ask clarifying questions to deepen your understanding.
- Paraphrase: Mentally paraphrase the information to ensure comprehension.
Methods for Efficient Recording of Information
- Abbreviations and Symbols: Use abbreviations and symbols to write faster.
- Structured Layouts: Organize your notes using bullet points, headings, and subheadings.
- Highlighting: Highlight key points and important information.
Balancing Listening and Writing
Striking a balance between listening and writing is essential. Focus on capturing the essence of the information rather than transcribing everything verbatim. This will help you stay engaged and avoid missing critical points.

Phase 3: Reviewing and Revising
Importance of Immediate Review
The third phase of focused note taking is Reviewing and Revising. Reviewing your notes immediately after the session helps reinforce the information and identify any gaps in understanding.
Techniques for Revising and Expanding Notes
- Clarify Points: Add additional details or explanations to unclear points.
- Organize Information: Rearrange your notes to create a logical flow of information.
- Cross-Referencing: Link related concepts and ideas across different sections of your notes.
Addressing Gaps in Understanding
Identify areas where your understanding is lacking and seek additional information or clarification. This proactive approach will enhance your comprehension and retention.
Phase 4: Summarizing and Synthesizing
Creating Concise Summaries
The fourth phase of focused note taking is Summarizing and Synthesizing. Summarizing involves condensing the information into concise, manageable chunks. This helps in retaining the core message and key points.
Connecting Ideas and Concepts
Synthesizing involves connecting different ideas and concepts to form a cohesive understanding. Look for patterns, relationships, and overarching themes in your notes.
Developing a Holistic Understanding
By summarizing and synthesizing the information, you develop a holistic understanding of the subject matter. This deeper comprehension is essential for applying the knowledge effectively.
Phase 5: Applying and Assessing
Using Notes for Practical Application
The final phase of focused note taking is Applying and Assessing. Using your notes for practical application solidifies your understanding and helps in retaining the information long-term.
- Practice Problems: Apply concepts to practice problems or real-world scenarios.
- Discussions: Engage in discussions or study groups to test your understanding.
- Projects: Use your notes as a reference for projects or assignments.
Self-Assessment Techniques
Regularly assess your understanding and note-taking effectiveness. Self-assessment techniques include quizzes, flashcards, and self-reflection.
| Related: Effective memorization techniques for students
Refining Note-Taking Strategies Based on Outcomes
Based on your self-assessment, refine your note-taking strategies. Identify what works best for you and make necessary adjustments to improve your focused note taking skills.

Different Note-Taking Techniques
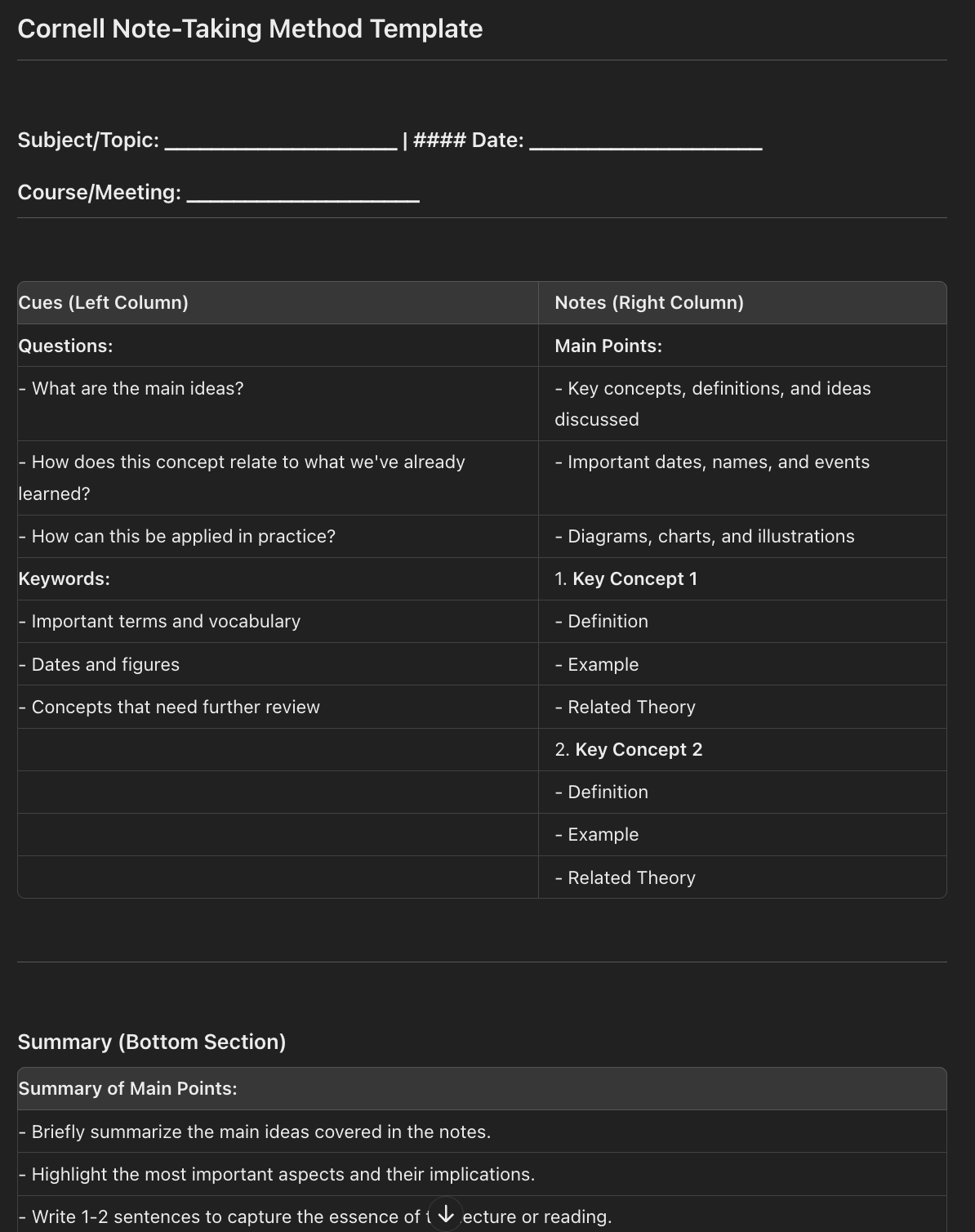
Cornell Note-Taking Method
The Cornell Note-Taking Method is a popular technique developed by Professor Walter Pauk at Cornell University. This method is designed to help students organize their notes efficiently and enhance their study sessions.
Structure of Cornell Notes
- Note-Taking Area: The main section for recording lecture notes.
- Cue Column: A smaller column on the left for keywords, questions, and prompts.
- Summary Section: A section at the bottom of the page for summarizing the main points.
Benefits of Cornell Notes
- Active Summarizing: Encourages summarizing information, which aids in better comprehension.
- Intentional Note-Taking: Promotes focus and intentionality by requiring the recording of key points.
- Revision-Ready: The format is ideal for reviewing and self-testing.
Mind Mapping
Mind Mapping is a visual note-taking technique that involves creating diagrams to represent ideas and concepts. This method is particularly useful for brainstorming and organizing complex information.
How to Create a Mind Map
- Central Idea: Start with the main topic in the center.
- Branches: Draw branches from the central idea to subtopics.
- Keywords: Use keywords and images to represent ideas.
- Connections: Draw lines to connect related ideas.
Benefits of Mind Mapping
- Visual Representation: Helps in visualizing relationships between concepts.
- Enhanced Memory: The use of images and colors can improve memory retention.
- Creativity Boost: Encourages creative thinking and idea generation.
Outline Method
The Outline Method is a hierarchical note-taking technique that organizes information in a structured format. This method is ideal for capturing detailed and organized notes.
Structure of the Outline Method
- Main Topics: Use Roman numerals for main topics.
- Subtopics: Use letters and numbers for subtopics and details.
Benefits of the Outline Method
- Organized Information: Provides a clear and organized structure.
- Easy Review: Simplifies the review process by breaking down information into manageable sections.
- Flexibility: Can be adapted to different types of content and subjects.
Charting Method
The Charting Method involves creating tables or charts to organize information. This method is particularly useful for subjects that involve comparisons or data.
How to Use the Charting Method
- Columns and Rows: Create columns for categories and rows for details.
- Headings: Use headings to label each column.
- Data Entry: Fill in the details under each heading.
Benefits of the Charting Method
- Comparison: Facilitates easy comparison of information.
- Clarity: Provides a clear visual representation of data.
- Efficiency: Helps in quickly locating specific information.
Tips for Enhancing Focused Note-Taking
Tools and Technologies
Leverage tools and technologies to enhance your note-taking process. Digital note-taking apps, voice recorders, and mind-mapping software can be valuable resources.
Developing a Personalized System
Develop a personalized note-taking system that suits your learning style and preferences. Experiment with different methods and find what works best for you.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Common challenges in focused note-taking include distractions, information overload, and lack of organization. Address these challenges by creating a conducive environment, breaking down information into manageable chunks, and maintaining a structured layout.
Conclusion
Mastering the five phases of focused note-taking can significantly enhance your learning and retention capabilities. By Previewing and Planning, Active Listening and Recording, Reviewing and Revising, Summarizing and Synthesizing, and Applying and Assessing, you can develop a comprehensive and effective note-taking system.
Implement these strategies and experience the long-term benefits of focused note taking in your academic and professional endeavors. This comprehensive article should provide valuable insights into the five phases of focused note-taking while naturally integrating the keyword throughout the content.



